How Crypto Works: A Comprehensive Guide Introduction
Introduction
The fashionability of cryptocurrency has soared in recent times. The working of crypto has fully changed the expressway we view deals and money. Although the working of crypto uses convoluted technology, it’s accessible with sufficient foundational knowledge. In this blog, we will give an introductory elucidation of the workings of crypto.
Describe cryptocurrency.
One kind of digital currency is cryptocurrency. It functions apart from conventional banks. Blockchain technology is essential to the operation of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency only exists in digital form, as opposed to actual currency.
What Is the Process of Cryptocurrency?
Blockchain technology is the foundation for cryptocurrency’s operation. It’s a decentralized tally that keeps track of deals. It is a decentralized ledger that keeps track of transactions. A network of computers verifies each transaction, and they use cryptography to protect the transactions.
Important Elements of Cryptocurrency
Let us examine the main elements of crypto to get how it operates:
- Blockchain Technology The foundation of cryptocurrencies is blockchain. It securely and openly documents transactions.
- Encryption using CryptographyOne important component of cryptography is security. Thanks to cryptography, transactions are safe and unchangeable.
Working of Crypto Network Decentralization:
Unlike conventional fiscal institutions, cryptocurrency functions on a decentralized network, which indicates that a single authority doesn’t govern it.
Mining ProcessMining is essential to how cryptocurrency operates. Miners validate transactions and add them to the blockchain by resolving challenging mathematical puzzles.
Digital wallets are where users save their cryptocurrency. These wallets may be hardware or software-based systems.
Step-by-Step Working of Crypto
Let’s break down the working of crypto step by step:
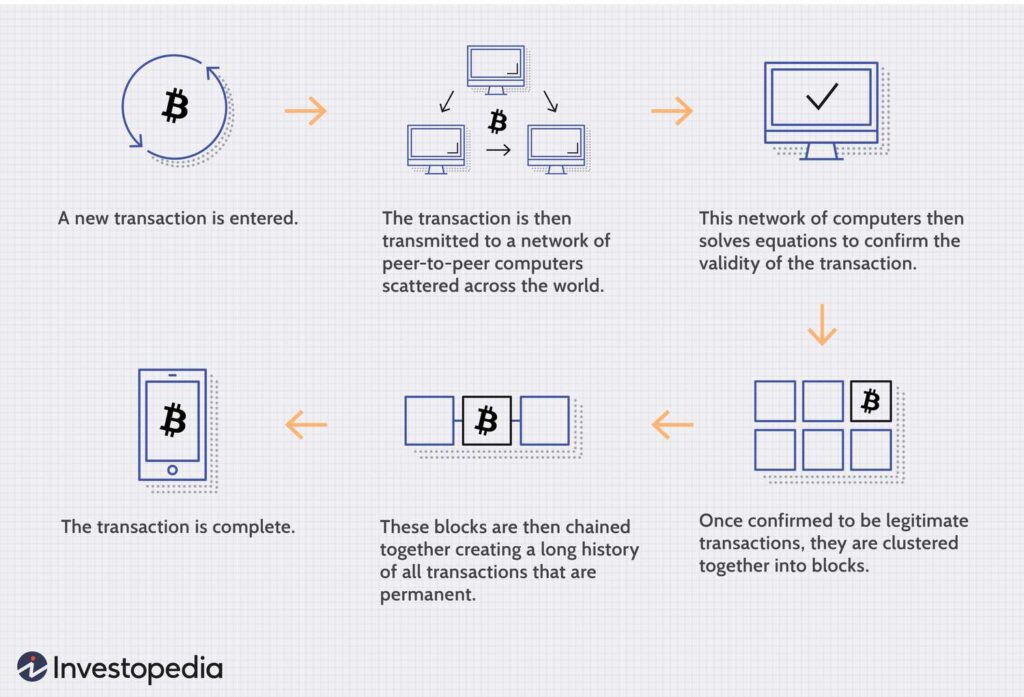
1. Transaction Initiation
The process begins when a stoner decides to shoot cryptocurrency to another stoner. This could be done for several purposes, similar to investing, transferring plutocrats, or buying commodities. The sender specifies the quantum to be transferred as well as the philanthropist’s portmanteau address. The sale is also inked using the sender’s private key, icing its integrity and security. The procedure begins when a stoner decides to shoot cryptocurrency to another stoner.
2. Transaction Verification
The transaction is broadcast to the entire network as soon as it’s started. Several computers, appertained to as bumps, make up the network and cooperate to corroborate the sale. These bumps corroborate that the sale conforms with blockchain regulations and that the sender has enough plutocrats. To make sure the sale is authentic and unaltered, they employ cryptographic ways.
3. Block Creation
A block is created by grouping the validated sale with other deals following a successful verification. In substance, a block is an assemblage of deals that are all recorded together before being added to the blockchain. Every block includes all sale information, references to the block before it, and a unique identifier known as a hash.
4. Mining Process
A technique called mining is needed to add a block to the blockchain after it has been created. Actors in the network, known as miners, contend to figure out a gruelling cryptographic mystery. This procedure, occasionally appertained to as Proof of Work( PoW) or similar agreement processes, necessitates a large quantum of processing power. The block is added to the blockchain and cryptocurrency is awarded to the first miner to break the problem.
5. Transaction Completion
The transaction is regarded as completed and irrevocable once the block is uploaded to the blockchain. This indicates that the blockchain now shows the streamlined balance and that the receiver is now the legal proprietor of the transferred bitcoin. Because blockchain technology is decentralized, it’s nearly impossible to change or reverse a sale, which ensures security and trustability.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
The working of crypto offers several benefits, such as:
-
Security
Because cryptocurrency relies on encryption methods, transactions are extremely safe. Sensitive data is shielded from unwanted access by encryption. It guarantees that the transaction data are only accessible by the designated receiver. Because of this, hackers find it very difficult to change or steal money.
-
Transparency
Transparency is one of the main characteristics of cryptocurrencies. Every transaction is documented on the blockchain, a public ledger. This makes it possible for anybody to check transactions at any moment. Consequently, transparency helps to prevent fraudulent actions and fosters user trust.
-
Decentralization
There is no central authority in cryptocurrency. It is not controlled by a single entity, in contrast to traditional financial systems. Rather, transactions are managed by a dispersed network of computers. Users have more control over their money thanks to this decentralization, which also lowers the possibility of manipulation or meddling from the government.
-
Lower Transaction Fees
Transaction fees for cryptocurrencies are typically lower than those for conventional banking methods. For services like foreign transfers, banks and other financial institutions impose exorbitant fees. On the other hand, because cryptocurrency eliminates middlemen, consumers can send money at a much lower price. Because of this, it is a desirable choice for both people and companies trying to reduce transaction costs.
Challenges in the Working of Crypto
Despite its advantages, the working of crypto faces some challenges:
- Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile. - Regulatory Issues
Many governments have not yet regulated cryptocurrencies. - Security Risks
Although crypto is secure, hackers can still target exchanges and wallets.
Working of Crypto Popular Cryptocurrencies
Several cryptocurrencies exist today, but the most popular ones include:
- Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency. - Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum offers smart contracts in addition to digital currency. - Ripple (XRP)
Ripple focuses on fast international payments. - Litecoin (LTC)
Litecoin is similar to Bitcoin but offers faster transaction speeds.
Conclusion
The workings of cryptography are charming and dynamic. People find it interesting because it changes how plutocrat works. Among its multitudinous advantages are downgraded charges and brisk processes. still, there are several disadvantages as well, involving freight volatility and screen pitfalls. For several reasons, numerous companies and individuals are starting to look into cryptocurrencies. They want to take advantage of its eventuality indeed if they’re apprehensive of the pitfalls. As the world transitions to digital currency, it’s progressively important to comprehend how cryptocurrencies work. It helps individuals and companies make well-grassed opinions. With this information, they can save their fiscal advantage and pinch new openings.